Hey there, let me introduce you to a cognitive assessment test known as the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). This test is widely used in Asia, aimed at evaluating various cognitive functions. It consists of several tasks and measures different cognitive domains such as attention, memory, language, and visuospatial abilities. Let’s dive into the details of this assessment!
MoCA Test Features
The MoCA test comprises a set of questions and tasks that assess cognitive abilities. It has gained popularity among healthcare professionals, researchers, and educators due to its effectiveness and simplicity. With the aim of measuring cognitive impairment, it can assist in detecting early signs of cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
One of the strengths of the MoCA test is its ability to assess cognitive abilities beyond the scope of traditional screening tests. It covers a wide range of cognitive functions, making it a comprehensive tool for cognitive assessment.
How Does the MoCA Test Work?
The MoCA test consists of several tasks that assess different cognitive domains. Here are some of the tasks you may encounter during the assessment:
- Visuospatial and Executive Functioning
 One of the tasks evaluates visuospatial and executive functioning by asking the individual to draw a specific shape or connect numbers and letters in a specific order.
One of the tasks evaluates visuospatial and executive functioning by asking the individual to draw a specific shape or connect numbers and letters in a specific order.
- Attention and Working Memory
 This task measures attention and working memory. It may involve repeating a list of numbers or identifying a specific letter in a sequence of letters.
This task measures attention and working memory. It may involve repeating a list of numbers or identifying a specific letter in a sequence of letters.
- Language Abilities
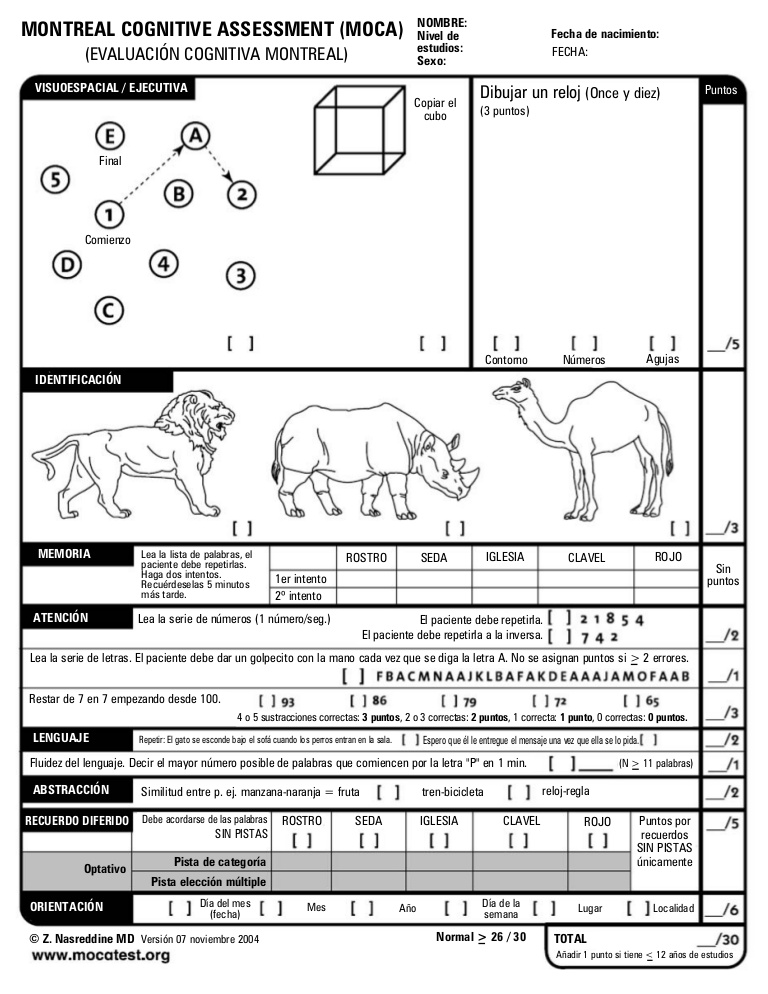 To assess language abilities, individuals may be asked to name objects, repeat sentences, or follow verbal instructions.
To assess language abilities, individuals may be asked to name objects, repeat sentences, or follow verbal instructions.
- Memory Recall
 This task evaluates memory recall by asking individuals to remember and repeat a series of words or recall specific information provided earlier in the test.
This task evaluates memory recall by asking individuals to remember and repeat a series of words or recall specific information provided earlier in the test.
- Abstract Reasoning
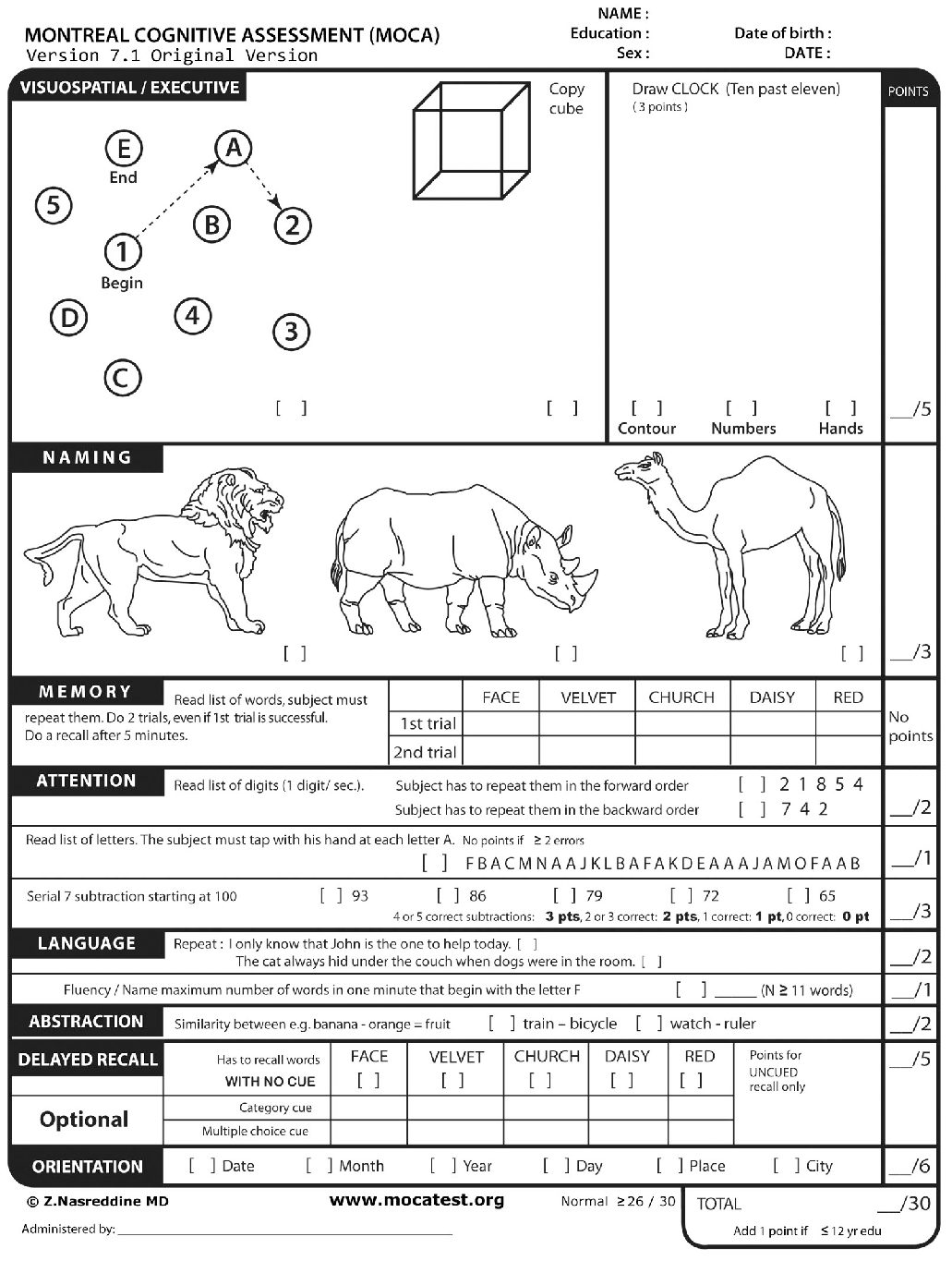 The MoCA test also assesses abstract reasoning abilities. This may involve solving problems, identifying patterns, or completing sequences.
The MoCA test also assesses abstract reasoning abilities. This may involve solving problems, identifying patterns, or completing sequences.
Scoring the MoCA Test
Each task in the MoCA test contributes to the overall score. The maximum possible score is 30, with a score of 26 or above generally considered normal. Scores below 26 may indicate cognitive impairment or decline.
It is important to note that the MoCA test should not be used as a definitive diagnostic tool but rather as an initial screening assessment. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional should follow if any concerns arise.
The Importance of the MoCA Test
The MoCA test plays a crucial role in identifying early signs of cognitive impairment and is particularly valuable in Asian countries where the aging population is increasing rapidly. Early detection allows for earlier intervention and management of cognitive decline, potentially improving the quality of life for affected individuals and their families.
It’s worth mentioning that the MoCA test has been subject to adaptation to meet the specific cultural and linguistic needs of different populations. For example, the Beijing version of the MoCA test is available in English for researchers and clinicians worldwide.
Conclusion
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is a widely-used cognitive assessment tool that helps healthcare professionals and researchers evaluate cognitive abilities. It assesses various cognitive domains such as attention, memory, language, and visuospatial abilities. The test provides valuable insights into cognitive health and helps identify potential cognitive impairment early on. Remember, if you have any concerns about your cognitive abilities or the cognitive abilities of a loved one, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation.