A1C: Understanding Your Blood Sugar Levels
As a healthcare professional, it is crucial to understand the importance of monitoring blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. One of the key measurements used to assess long-term blood sugar control is the A1C test. This test provides valuable insights into a person’s average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. A1C levels are expressed as a percentage and are used to diagnose and manage diabetes.
 The A1C Chart: A Helpful Tool for Diabetics
The A1C Chart: A Helpful Tool for Diabetics
The A1C chart is a useful visual representation that helps individuals with diabetes understand their blood sugar control. With the help of this chart, people can track their progress and make the necessary lifestyle changes to achieve their target A1C levels. Here’s how to read and interpret the A1C levels chart:
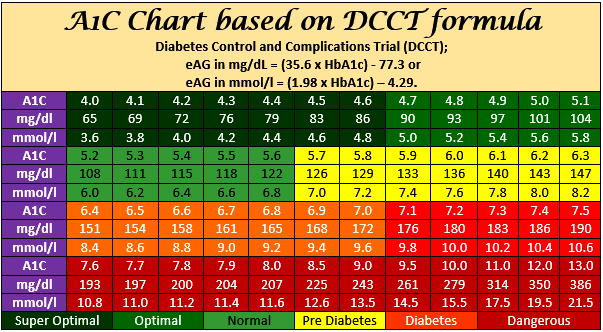 The A1C chart represents different A1C levels on the y-axis ranging from 4% to 15%, and it plots time on the x-axis. The chart shows the target range for A1C levels, which is typically below 7% for individuals with diabetes. It also highlights the hyperglycemic range (above the target) and hypoglycemic range (below the target).
The A1C chart represents different A1C levels on the y-axis ranging from 4% to 15%, and it plots time on the x-axis. The chart shows the target range for A1C levels, which is typically below 7% for individuals with diabetes. It also highlights the hyperglycemic range (above the target) and hypoglycemic range (below the target).
Understanding A1C Conversion
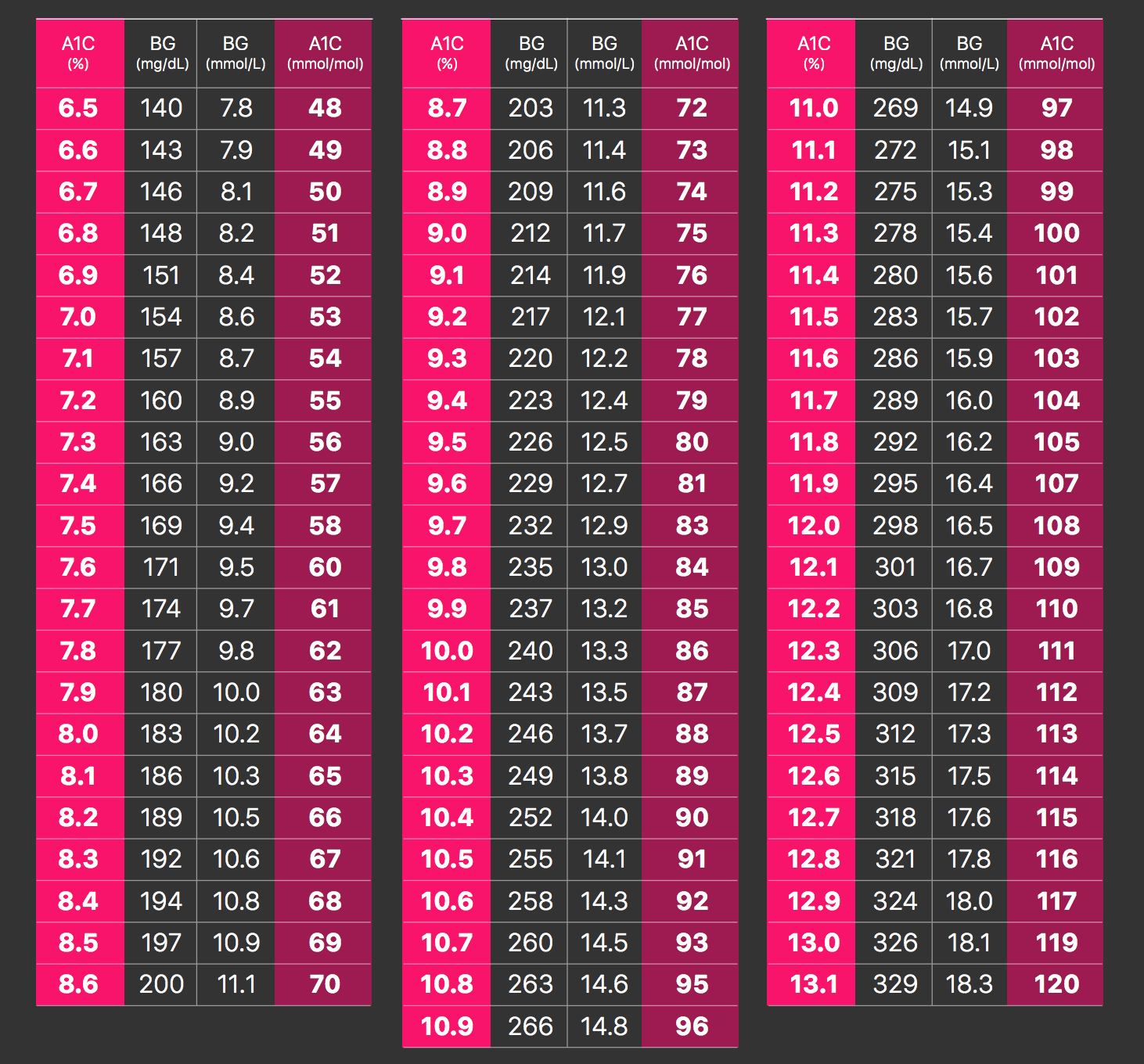
Converting A1C levels to an estimated average glucose (eAG) level can help individuals better understand their blood sugar control. The conversion between A1C and eAG is based on the relationship between average blood sugar levels and the percentage of hemoglobin with glucose attached to it (glycated hemoglobin).
 Here’s how to interpret the A1C chart for conversion to eAG:
Here’s how to interpret the A1C chart for conversion to eAG:
- An A1C level of 6% corresponds to an eAG level of approximately 126 mg/dL.
- An A1C level of 7% corresponds to an eAG level of approximately 154 mg/dL.
- An A1C level of 8% corresponds to an eAG level of approximately 183 mg/dL.
Using the A1C Chart for Diabetes Management
The A1C chart serves as a valuable tool for diabetes management. By regularly monitoring and tracking A1C levels, individuals can gain insights into their blood sugar control and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plans. Here are a few tips to utilize the A1C chart effectively:
 ### 1. Set Personal A1C Goals:
### 1. Set Personal A1C Goals:
Discuss with your healthcare provider and determine an appropriate A1C target range based on your individual needs and medical history.
2. Regular Blood Sugar Testing:
Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM). This will help you understand how your daily habits affect your blood sugar control.
3. Track Your A1C Levels:
Record your A1C levels over time to identify any patterns or trends. This will enable you to make informed decisions regarding your diabetes management plan.
Conclusion
The A1C chart is an essential tool for individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals alike. It helps in understanding blood sugar control and setting appropriate treatment goals. By consistently monitoring A1C levels and making necessary adjustments, individuals with diabetes can improve their overall health and reduce the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
 Remember, diabetes management is a collaborative effort between patients and healthcare providers. By utilizing resources such as the A1C chart, individuals can actively participate in their own care and work towards achieving optimal blood sugar control.
Remember, diabetes management is a collaborative effort between patients and healthcare providers. By utilizing resources such as the A1C chart, individuals can actively participate in their own care and work towards achieving optimal blood sugar control.
References:
- http://healthy-ojas.com/sites/default/files/diabetes/a1c-chart-dcct.png
- http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-GZwh9cAB-98/VeP2bJtJQUI/AAAAAAAAAYQ/FCMjLj7likE/s1600/A1c%2Blevels%2Bchart.jpg
- https://i.pinimg.com/736x/1f/e7/f7/1fe7f776e6182281960de7b27f0be03d--charts.jpg
- https://reporting.onedrop.today/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/a1c-chart.png